Elastic Load Balancer
- Regional Service
- Supports Multi AZ
- Spread load across multiple EC2 instances
- Separate public traffic from private traffic
- Health checks allow ELB to know which instances are working properly (done on a port and a route,
/healthis common) - Does not support weighted routing
If no targets are associated with the target groups => 503 Service Unavailable Using ALB & NLB, instances in peered VPCs can be used as targets using IP addresses.
Types
Classic Load Balancer (CLB) - deprecated
- Load Balancing to a single application
- Supports HTTP, HTTPS (layer 7) & TCP (layer 4)
- Health checks are HTTP or TCP based
- Provides a fixed hostname (xxx.region.elb.amazonaws.com)
Application Load Balancer (ALB)
- Load balancing to multiple applications (target groups) based on the request parameters
- Operates at Layer 7 (HTTP, HTTPS and WebSocket)
- Provides a fixed hostname (xxx.region.elb.amazonaws.com)
- ALB terminates the upstream connection and creates a new downstream connection to the targets (TCP termination)
- Security Groups can be attached to ALBs to filters requests
- Great for micro services & container-based applications (Docker & ECS)
- Client info is passed in the request headers
- Client IP => X-Forwarded-For
- Client Port => X-Forwarded-Port
- Protocol => X-Forwarded-Proto
- Target Groups
- Health checks are done at the target group level
- Target Groups could be
- EC2 instances - HTTP
- ECS tasks - HTTP
- Lambda functions - HTTP request is translated into a JSON event
- Private IP Addresses
- Listener Rules can be configured to route traffic to different target groups based on:
- Path (example.com/users & example.com/posts)
- Hostname (one.example.com & other.example.com)
- Query String (example.com/users?id=123&order=false)
- Request Headers
- Source IP address
The following cookie names are reserved by the ELB(Application LB) (AWSALB, AWSALBAPP, AWSALBTG).
Network Load Balancer (NLB)
- Operates at Layer 4 (TCP, UDP)
- Can handle millions of request per seconds (extreme performance)
- Lower latency ~ 100 ms (vs 400 ms for ALB)
- 1 static public IP per AZ (vs a static hostname for CLB & ALB)
- Elastic IP can be assigned to NLB (helpful for whitelisting specific IP)
- Maintains the same connection (TCP or UDP) from client all the way to the target application
- No security groups can be attached to NLBs. Since they operate on layer 4, they cannot see the data available at layer 7. They just forward the incoming traffic to the right target group as if those requests were directly coming from client. So, the attached instances must allow TCP traffic on port 80 from anywhere.
- Within a target group, NLB can send traffic to
- EC2 instances
- If you specify targets using an instance ID, traffic is routed to instances using the primary private IP address
- IP addresses
- Used when you want to balance load for a physical server having a static IP.
- Application Load Balancer (ALB)
- Used when you want a static IP provided by an NLB but also want to use the features provided by ALB at the application layer.
- EC2 instances
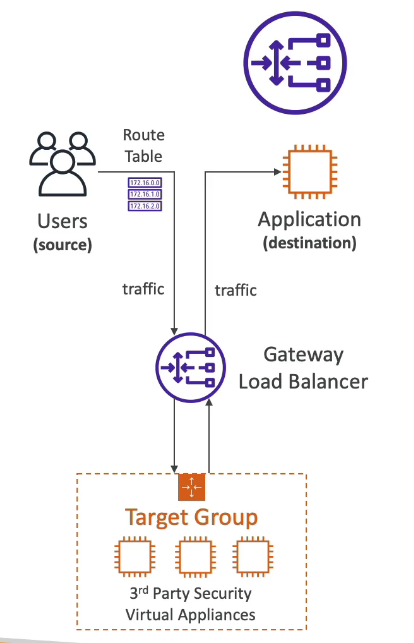
Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB)
-
Operates at layer 3 (Network layer) - IP Protocol
-
Used to route requests to a fleet of 3rd party virtual appliances like Firewalls, Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS), etc.
-
Performs two functions:
- Transparent Network Gateway (single entry/exit for all traffic)
- Load Balancer (distributes traffic to virtual appliances)
-
Uses GENEVE protocol
-
Target groups for GWLB could be
- EC2 instances
- IP addresses
Only Network Load Balancer provides both static DNS name and static IP. While, Application Load Balancer provides a static DNS name but it does NOT provide a static IP. The reason being that AWS wants your Elastic Load Balancer to be accessible using a static endpoint, even if the underlying infrastructure that AWS manages changes.
Sticky Sessions (Session Affinity)
- Requests coming from a client is always redirected to the same instance based on a cookie. After the cookie expires, the requests coming from the same user might be redirected to another instance.
- Only supported by CLB & ALB because the cookie can be seen at layer 7
- Used to ensure the user doesn’t lose his session data, like login or cart info, while navigating between web pages.
- Stickiness may cause load imbalance
- Cookies could be
- Application-based (TTL defined by the application)
- Load Balancer generated (TTL defined by the load balancer)
- ELB reserved cookie names (should not be used)
- AWSALB
- AWSALBAPP
- AWSALBTG
Cross-zone Load Balancing
Allows ELBs in different AZ containing unbalanced number of instances to distribute the traffic evenly across all instances in all the AZ registered under a load balancer.
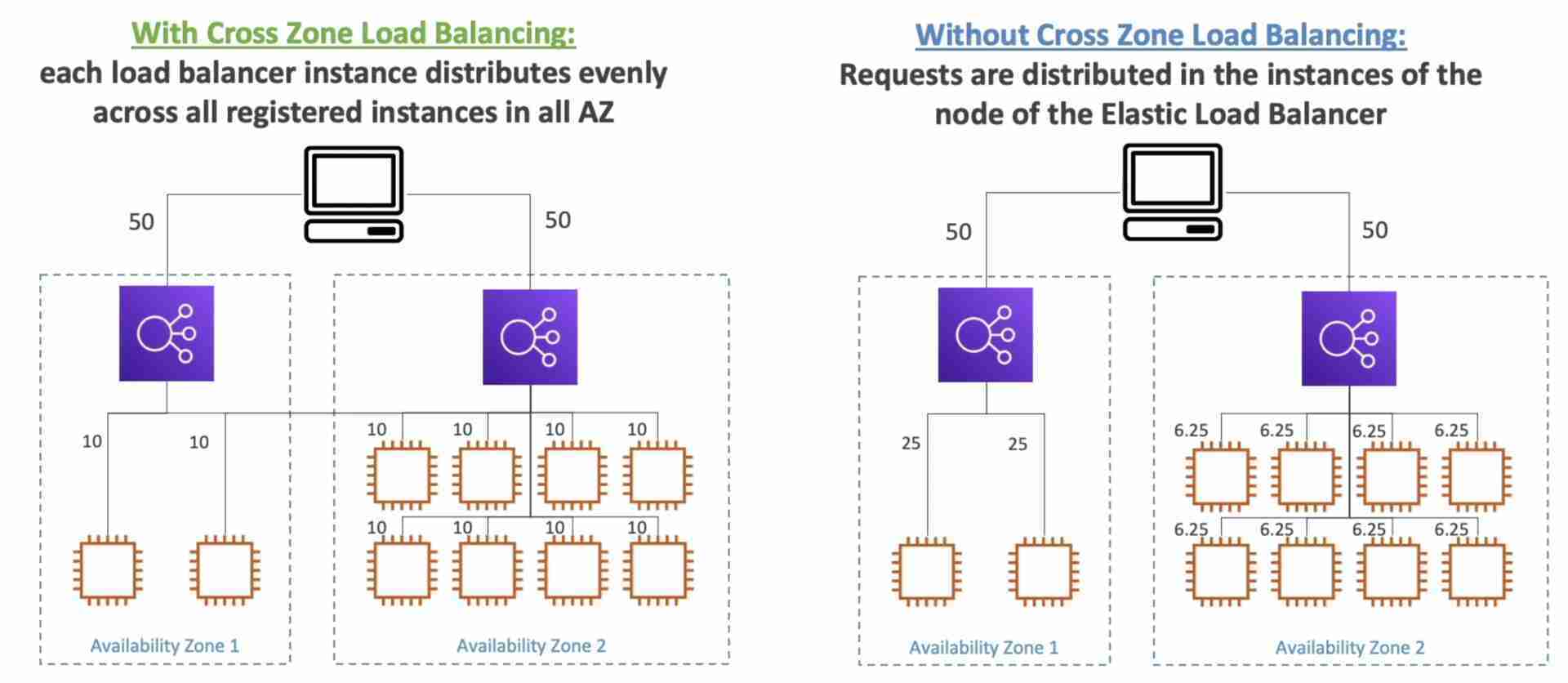
Supported Load Balancers
- Classic Load Balancer
- Disabled by default
- No charges for inter AZ data
- Application Load Balancer
- Always on (can’t be disabled)
- No charges for inter AZ data
- Network Load Balancer
- Disabled by default
- Charges for inter AZ data
In-Flight Encryption
- Use an NLB with a TCP listener & terminate SSL on EC2 instances
- Use an ALB with an HTTPS listener, install SSL certificates on the ALB & terminate SSL on the ALB
- Communication between ALB & EC2 instances can happen over HTTP inside the VPC
- Server Name Indication (SNI)
- SNI allows us to load multiple SSL certificates on one Load Balancer to serve multiple websites securely
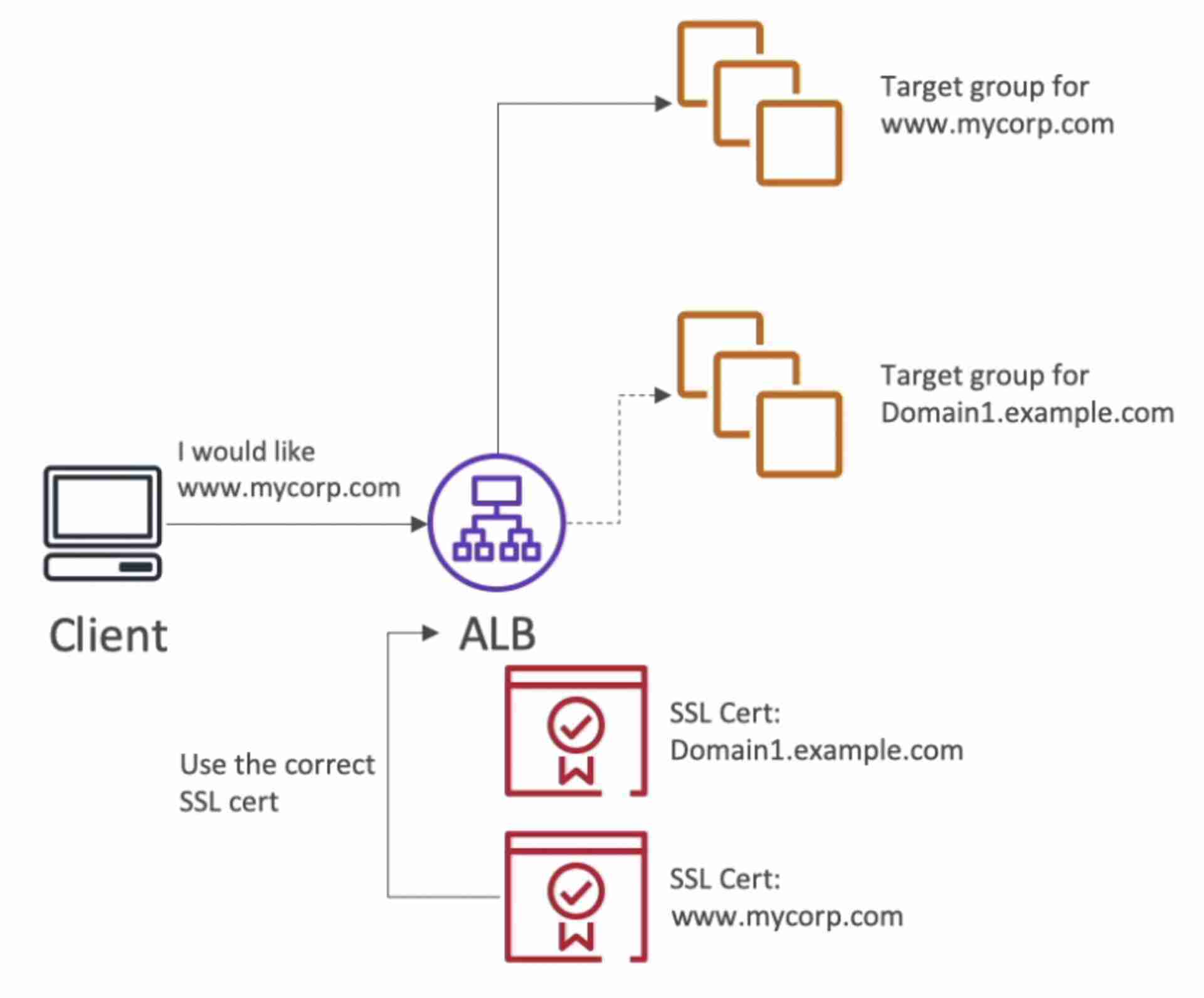
- Only works for ALB & NLB (CLB only supports one SSL certificate)
- Newer protocol, not every client supports it yet
- Supported in CloudFront also
Connection Draining (De-registration Delay)
- When an instance is to be de-registered from the ELB, the in-flight requests being served by that instance are given some pre-defined time to complete before the ELB de-registers it.
- ELB stops sending new requests to the EC2 instance which is de-registering
- Set manually (0 to 3600 seconds) (default: 300 seconds)
For instances behind an ELB and using ASG, increase the de-registration delay to ensure that the in-flight requests are completed before the ELB deregisters an instance which is to be terminated by the ASG.
Access Logs
- Captures detailed information about requests sent to the load balancer
- Used to analyze traffic patterns and troubleshoot issues
- Disabled by default
Misc
-
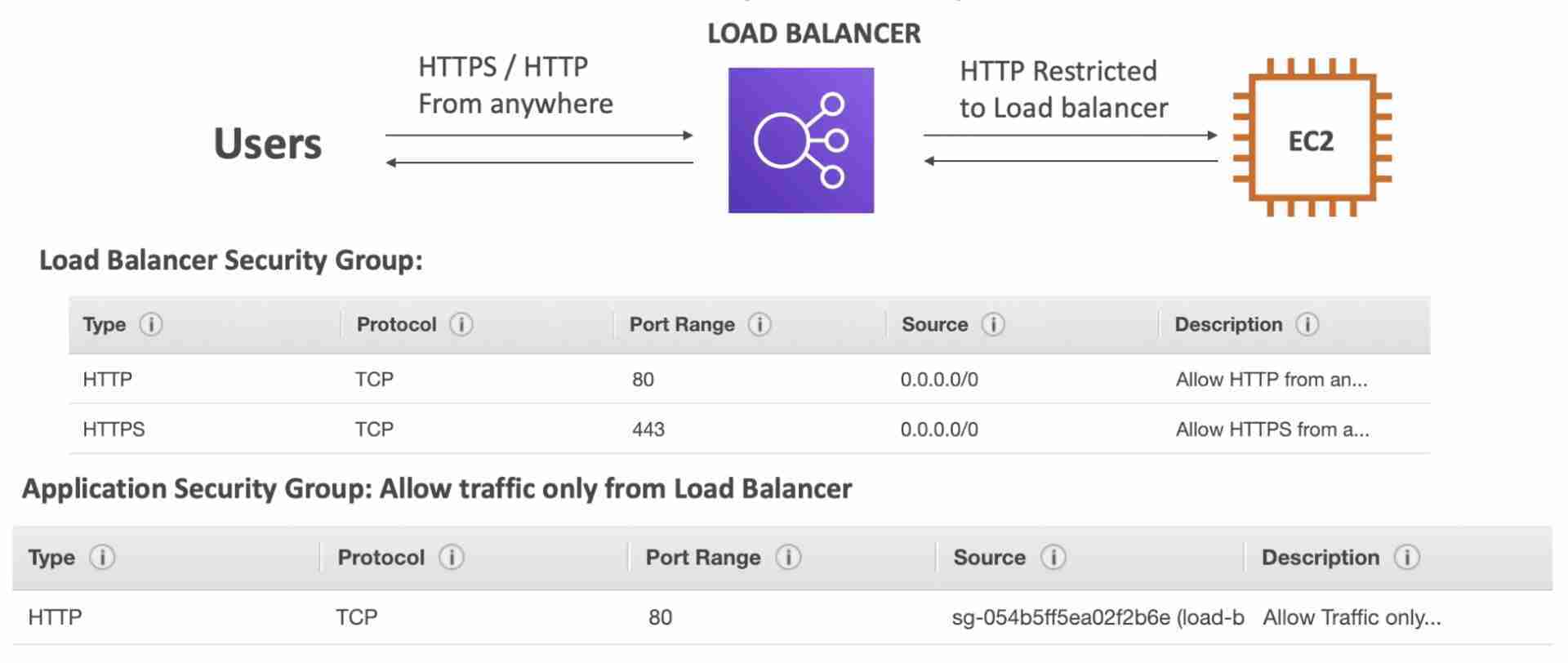
Security Groups for a public facing ELB
- ELB will be publicly available on the internet, so it’s security group should allow HTTP and HTTPS traffic from anywhere. EC2 should only allow traffic from the ELB, so the its security group should allow HTTP requests from ELB’s security group.